The VC Model is Broken, but How Broken is it?
Welcome back to my newsletter where I highlight one Venture Capital Concept, one useful framework, and many resources about the topic.
Most recent life Update: So it’s been a while since I’ve published a newsletter. I’ve taken a bigger role at the firm I’m at (Bloom Co. Capital) in Houston, Texas. The experience from seed to IPO has been insane
I’m Head of Venture Capital Investments and Operations
We currently have a diverse client base from CPG, Climate tech, Gaming, and more (Valued at $500MM). We also advise on some alternative investments in the real estate space.
One thing I am (REAL) and one thing I’m not (a Harvard grad who thinks they have it all figured.
I am very active on TikTok; however, check me out: Follow me on tiktok
1. Useful Life Framework: The Venture Capital Reality Check
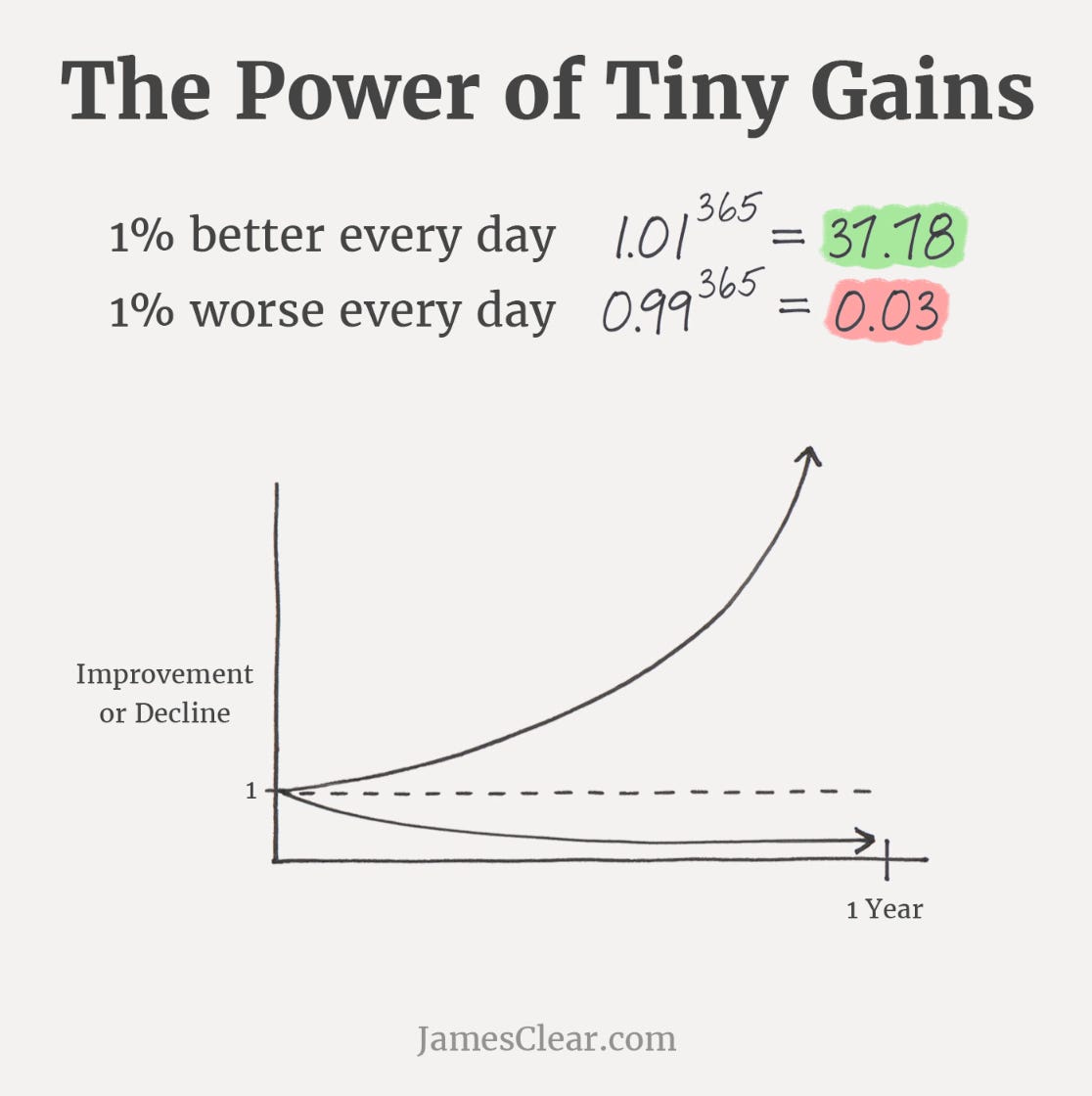
Key Principles: Remember anything above zero. Compounds over time…..
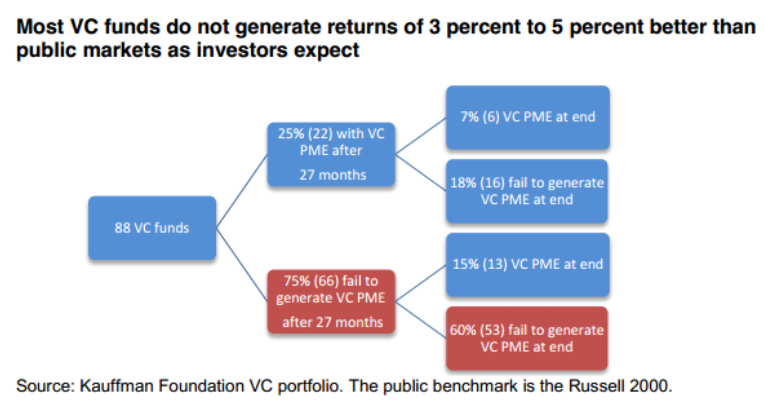
2. Insights: The VC Model Breakdown Analysis
2. Insights: The Current VC Model is Fundamentally Broken
The venture capital industry operates on assumptions that were valid 20 years ago but have become dangerously obsolete. Here's a five-tier breakdown of how the traditional VC model clashes with today's startup reality:
Tier 1: The Time Horizon Mismatch
Traditional VC Model: VCs expect 7-10 year fund cycles with clear exit opportunities through IPOs or acquisitions.
Real-Life Reality: Companies are staying private longer (average time to IPO increased from 4 years in 1999 to 11+ years today), IPO markets are increasingly volatile, and acquisition multiples have compressed significantly. Meanwhile, LPs are demanding returns faster than ever.
The Break: Fund managers are stuck holding illiquid positions in companies that can't exit, creating a liquidity crisis that forces premature decisions and suboptimal outcomes.
Tier 2: The Capital Efficiency Revolution
Traditional VC Model: Startups need massive capital injections to scale, requiring multiple large funding rounds with increasing valuations.
Real-Life Reality: Cloud infrastructure, no-code tools, and AI have dramatically reduced startup costs. Companies can now reach $1M+ ARR with less than $500K in funding, and many unicorns are being built with 80% less capital than their predecessors.
The Break: VCs are deploying too much capital into companies that don't need it, creating artificial growth pressure and unsustainable burn rates that actually harm long-term company health.
Tier 3: The Portfolio Construction Paradox
Traditional VC Model: The "spray and pray" approach - invest in 20-30 companies per fund, expect 1-2 to return the entire fund (the "power law").
Real-Life Reality: Market fragmentation and niche opportunities mean returns are more distributed. The mega-unicorn exits that historically drove power law returns are becoming rarer, while moderate successes ($50M-500M exits) are more predictable.
The Break: VCs are chasing lottery tickets instead of building sustainable portfolios, leading to over-investment in moonshot bets while ignoring profitable, steady-growth businesses.
Tier 4: The Valuation Inflation Trap
Traditional VC Model: Higher valuations signal market validation and create momentum for future rounds.
Real-Life Reality: Inflated valuations create unsustainable expectations for growth, make acquisitions nearly impossible (who wants to buy a $100M company that should be worth $20M?), and trap companies in "unicorn prison" where they can't exit profitably.
The Break: The valuation game has become divorced from fundamental business value, creating a generation of zombie unicorns that consume capital but can't deliver returns.
Tier 5: The Incentive Structure Catastrophe
Traditional VC Model: VCs are compensated through management fees (2%) and carried interest (20%), aligning their interests with fund performance.
Real-Life Reality: Management fees on billion-dollar funds provide comfortable income regardless of returns, while the 10-year carry timeline means partners can raise new funds before their previous ones prove successful or unsuccessful.
The Break: VCs are optimizing for fund-raising ability rather than investment returns, leading to larger funds, riskier bets, and a disconnect between what gets funded and what works.
The Bottom Line: The VC model worked when capital was scarce, exits were predictable, and building companies required massive upfront investment. Today's reality demands smaller, more targeted funds with longer time horizons, realistic valuations, and incentive structures that reward sustainable business building over financial engineering.
The market correction isn't just a cyclical downturn—it's the startup ecosystem finally rejecting a broken model that no longer serves entrepreneurs, investors, or innovation itself.
3. Resources: Essential VC Industry Analysis Tools
PitchBook Venture Capital Database - The leading financial data provider that tracks every aspect of the global capital markets—from limited partners and commitments to general partners, funds, investments, companies, and key players Venture Capital Database - PitchBook. Offers comprehensive historical data on fund performance, deal terms, and market trends going back decades.
CB Insights Research Platform - Market intelligence platform built from the ground up with AI that publishes annual "State of Venture" reports tracking global dealmaking trends CB InsightsCB Insights Research, including quarterly funding data, deal counts, and sector analysis State of Venture Q1'25 Report - CB Insights Research. Their historical trend archives provide deep insights into investment patterns over time.
NVCA Yearbook (National Venture Capital Association) - An important industry resource documenting trends and analysis of venture capital activity from the past year, capturing data about venture's role in fueling entrepreneurship in America, including statistics on the size and impact NVCA Yearbook - National Venture Capital Association - NVCA of the VC ecosystem with multi-year comparative data.
Bloomberg Terminal - A comprehensive financial data platform that includes venture capital data, private market research, and investment analysis tools. It offers access to proprietary data sets, market news, financial analysis, and investment research Top Venture Capital Data Providers with extensive historical databases for trend analysis.
Crunchbase - Used by VCs for deal histories and terms. What Tools do Associates at Venture Capital Firms use Everyday - 4Degrees, this platform provides comprehensive startup funding data, company profiles, and investment rounds dating back over a decade, making it invaluable for tracking long-term market evolution and investor behavior patterns.
Thanks for reading, I hope to see you back soon
Follow me on X: Follow me on X
My TikTok (Startups/VC Content) 45k: Tiktok
My LinkedIn: LinkedIn
Email: chrisgonzales@bloomcocapital.com
Deal flow (If interested):
The AirCraft Company
Hybrid-electric regional aircraft with wheelchair access + AI single-pilot. $430B+ market, aging fleet crisis, zero competition.
Traction: 40 aircraft LOI, Air New Zealand (30+ potential), flight sim complete.
Ask: $2M SEED → $3M Series A. 13% of 8K-20K aircraft needed @ $18M/unit. Deck: The AirCraft Company
Maestro
Viral music game turning players into orchestra conductors. 225M+ social views, >$1M in 3 months (VR only), expanding to 1B+ devices.
Traction: 4.8/5 rating, 20% DLC conversion, 106min playtime (4x industry avg), Meta Game of the Year.
Ask: €4M @ €22M pre. Platform expansion + IP acquisition. 15x-40x projected returns.
Deck: Maestro